In one my project there was a requirement from client to use Multiple Data Source like DB2, MySQL, Postgres, MariaDB within the same Spring Boot Application which should be using single configuration file with a data source connection pooling mechanism. So here in this example we are going to see how we can achieve the same.
Prerequisites To complete this example:
- An IDE
- JDK 11+ installed with JAVA_HOME configured appropriately
- Apache Maven 3.8.1+
Here are the Steps:
1. Create a maven project using SpringBoot and add the below Dependencies in pom.xml. Here we have added mySql connector for mySql datasource, postgresql for postgres data source and mariadb-java-client for mariadb data source.
<dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.postgresql</groupId><artifactId>postgresql</artifactId><scope>runtime</scope></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.mariadb.jdbc</groupId><artifactId>mariadb-java-client</artifactId><version>2.5.2</version></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId><artifactId>lombok</artifactId><optional>true</optional></dependency><dependency><groupId>mysql</groupId><artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId></dependency>
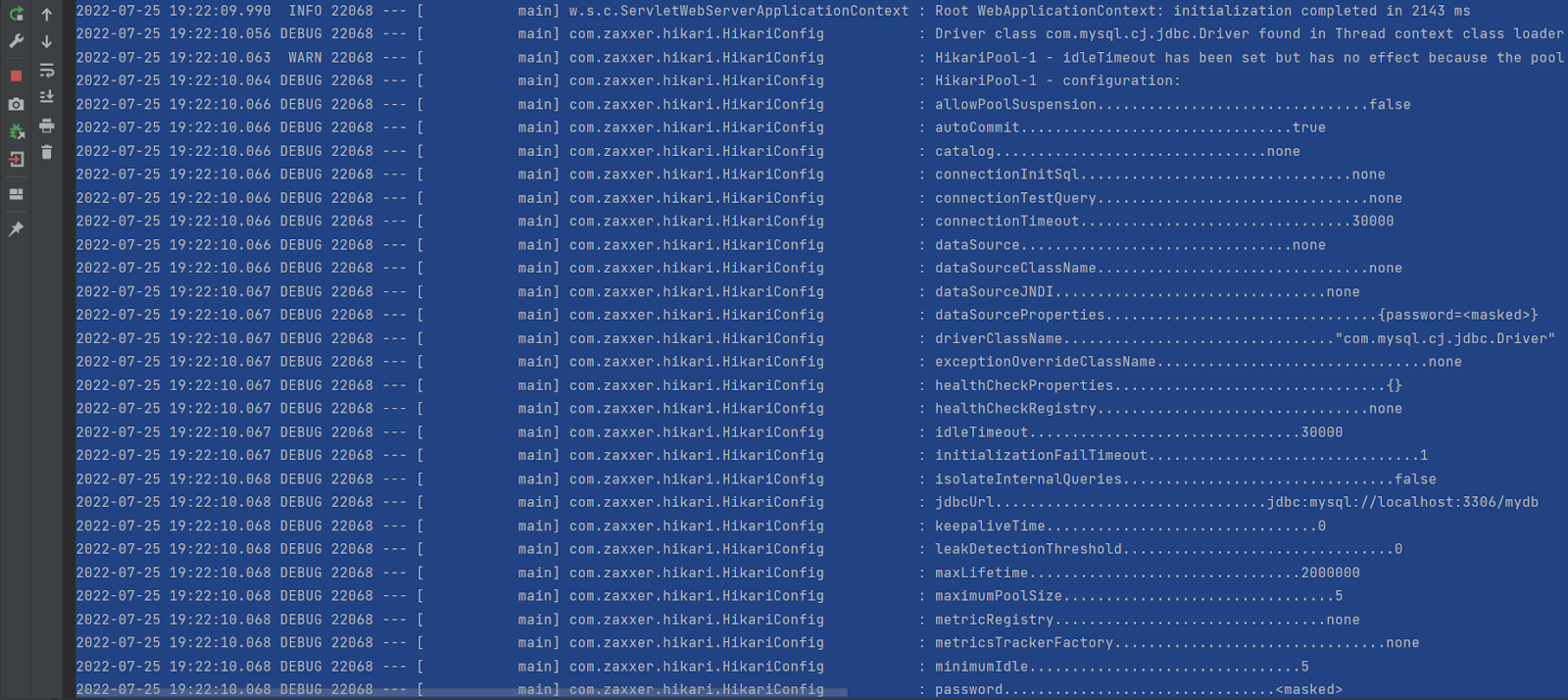
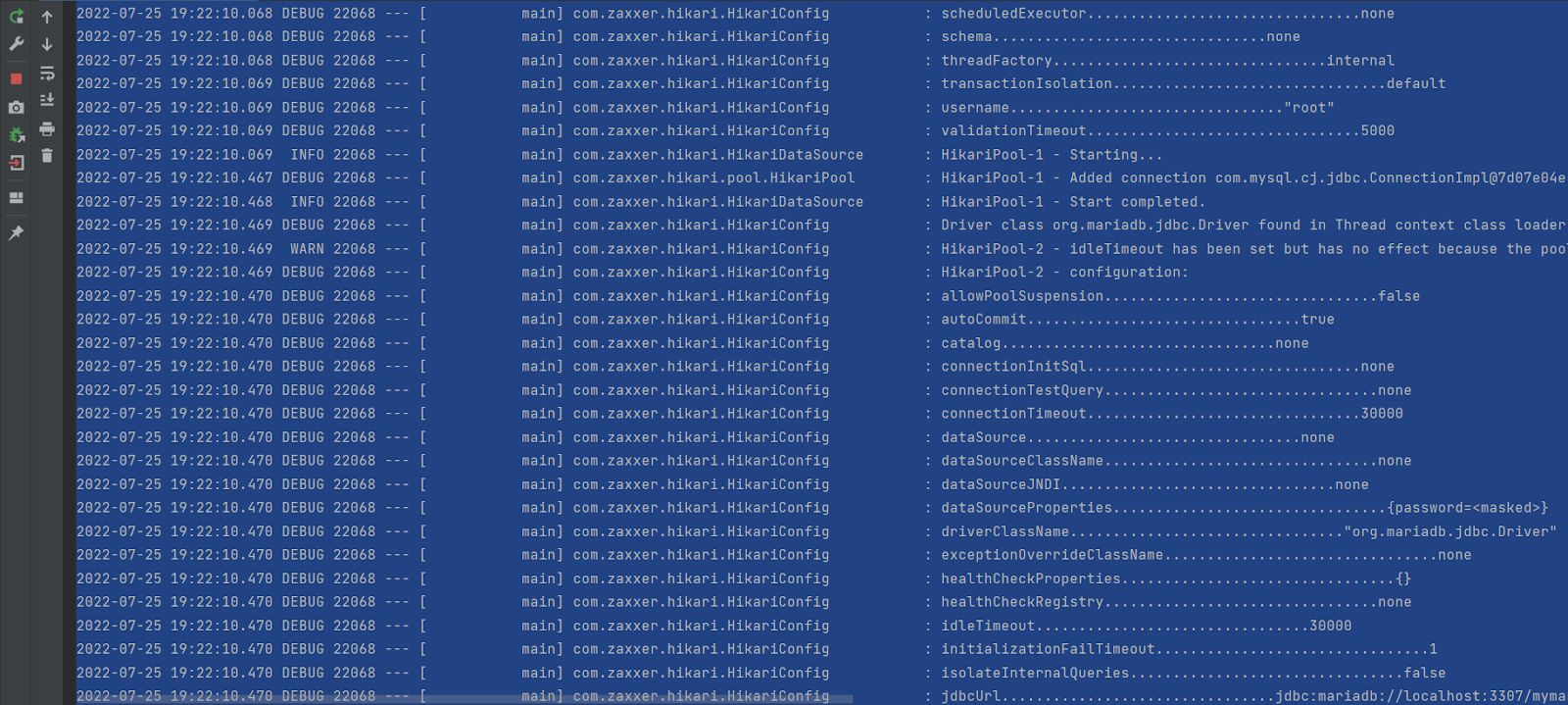
2. Provide the data source configuration properties for each data sources used by application like in this example we are using mySql , postgres and mariadb data source in application.properties file like shown below:
#MYSql DataSource Propertiesdb.configurations.mysqldb.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mydbdb.configurations.mysqldb.username=rootdb.configurations.mysqldb.password=rootdb.configurations.mysqldb.driver=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driverdb.configurations.mysqldb.maximumPoolSize=5db.configurations.mysqldb.minimumIdle=5db.configurations.mysqldb.idleTimeout=30000db.configurations.mysqldb.maxLifetime=2000000db.configurations.mysqldb.connectionTimeout=30000#Postgreys DataSource Propertiesdb.configurations.mypostgrey.url=jdbc:postgresql://localhost:5432/mypostgresdb.configurations.mypostgrey.username=postgresdb.configurations.mypostgrey.password=postgresdb.configurations.mypostgrey.driver=org.postgresql.Driverdb.configurations.mypostgrey.maximumPoolSize=5db.configurations.mypostgrey.minimumIdle=5db.configurations.mypostgrey.idleTimeout=30000db.configurations.mypostgrey.maxLifetime=2000000db.configurations.mypostgrey.connectionTimeout=30000#MariaDB DataSource Propertiesdb.configurations.mymaria.url=jdbc:mariadb://localhost:3307/mymariadbdb.configurations.mymaria.username=rootdb.configurations.mymaria.password=rootdb.configurations.mymaria.driver=org.mariadb.jdbc.Driverdb.configurations.mymaria.maximumPoolSize=5db.configurations.mymaria.minimumIdle=5db.configurations.mymaria.idleTimeout=30000db.configurations.mymaria.maxLifetime=2000000db.configurations.mymaria.connectionTimeout=30000
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "db")
@Component
@Data
public class DataBaseConfig {
private String url;
private String username;
private String driver;
private String password;
private String maximumPoolSize;
private String minimumIdle;
private String idleTimeout;
private String maxLifetime;
private String connectionTimeout;
private Map<String, DataBaseConfig> configurations = new HashMap<>();
DataSource createDataSource() {
HikariConfig config = new HikariConfig();
config.setJdbcUrl(url);
config.setUsername(username);
config.setPassword(password);
config.setDriverClassName(driver);
config.setMaximumPoolSize(Integer.parseInt(maximumPoolSize));
config.setMinimumIdle(Integer.parseInt(minimumIdle));
config.setIdleTimeout(Long.parseLong(idleTimeout));
config.setMaxLifetime(Long.parseLong(maxLifetime));
config.setConnectionTimeout(Long.parseLong(connectionTimeout));
HikariDataSource dataSource = new HikariDataSource(config);
return dataSource;
}
Map<Object, Object> createTargetDataSources() {
Map<Object, Object> result = new HashMap<>();
configurations.forEach((key, value) -> result.put(key, value.createDataSource()));
return result;
}
}
public class MultiRoutingDataSource extends AbstractRoutingDataSource {@AutowiredEnvironment env;private final String DEFAULT_LOOKUP_KEY = "test.db.defaultLookUpKey";@Overrideprotected Object determineCurrentLookupKey() {String defaultLookUpkey = env.getProperty(DEFAULT_LOOKUP_KEY);if (DBContextHolder.getDataBaseSite() == null) {logger.info("Inside If loop MultiRoutingDataSource defaultLookUpkey :" + defaultLookUpkey);if (defaultLookUpkey.isEmpty() == true) {throw new DataSourceLookUpException("Default Look Up key can not be Null or Empty, Please provide default lookup key in configuration file !!!");} else {return defaultLookUpkey.toString();}} else {return DBContextHolder.getDataBaseSite().toString();}}}
5. In a PersistenceConfiguration class define beans of type DataSource, LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean and PlatformTransactionManager, set the hibernet properties and scan the base package.
@Configuration
@EnableJpaRepositories(basePackages = "com.*",
entityManagerFactoryRef = "multiEntityManager",
transactionManagerRef = "multiTransactionManager")
public class PersistenceConfiguration {
@Autowired
DataBaseConfig dataBaseConfig;
private final String PACKAGE_SCAN = "com.*";
@Bean
DataSource multiRoutingDataSource() {
MultiRoutingDataSource dataSource = new MultiRoutingDataSource();
dataSource.setTargetDataSources(dataBaseConfig.createTargetDataSources());
return dataSource;
}
@Bean
LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean multiEntityManager() {
LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean em = new LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean();
em.setDataSource(multiRoutingDataSource());
em.setPackagesToScan(PACKAGE_SCAN);
HibernateJpaVendorAdapter vendorAdapter = new HibernateJpaVendorAdapter();
em.setJpaVendorAdapter(vendorAdapter);
em.setJpaProperties(hibernateProperties());
return em;
}
@Bean
PlatformTransactionManager multiTransactionManager() {
JpaTransactionManager transactionManager = new JpaTransactionManager();
transactionManager.setEntityManagerFactory(
multiEntityManager().getObject());
return transactionManager;
}
LocalSessionFactoryBean dbSessionFactory() {
LocalSessionFactoryBean sessionFactoryBean = new LocalSessionFactoryBean();
sessionFactoryBean.setDataSource(multiRoutingDataSource());
sessionFactoryBean.setPackagesToScan(PACKAGE_SCAN);
sessionFactoryBean.setHibernateProperties(hibernateProperties());
return sessionFactoryBean;
}
private Properties hibernateProperties() {
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.put("hibernate.show_sql", true);
properties.put("hibernate.format_sql", true);
properties.put("hibernate.dialect", "org.hibernate.dialect.MySQL5InnoDBDialect");
return properties;
}
}
try {
switch (client) {
case "mysqldb":
case "mypostgrey":
case "mymaria":
DBContextHolder.setDataBaseSite(client);
if (name == null) {
countryRepository.findAll().forEach(countries::add);
} else {
countryRepository.findCountriesByname(name).forEach(countries::add);
}
if (countries.isEmpty()) {
return new ResponseEntity<>(HttpStatus.NO_CONTENT);
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
return new ResponseEntity<>(null, HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR);
}
- request and response for mySql data source in postman Get request
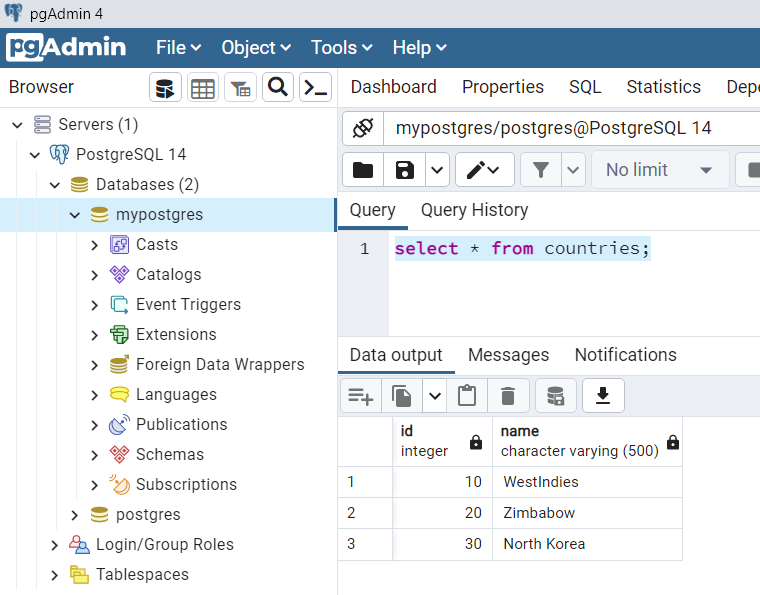
Open pgAdmin Console and execute the below query, we can see we got the correct response from our Rest API getCountries.
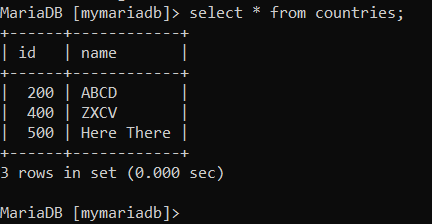
- request and response for mariadb data source in postman Get request














0 Comments